HBase BulkLoad
Page content
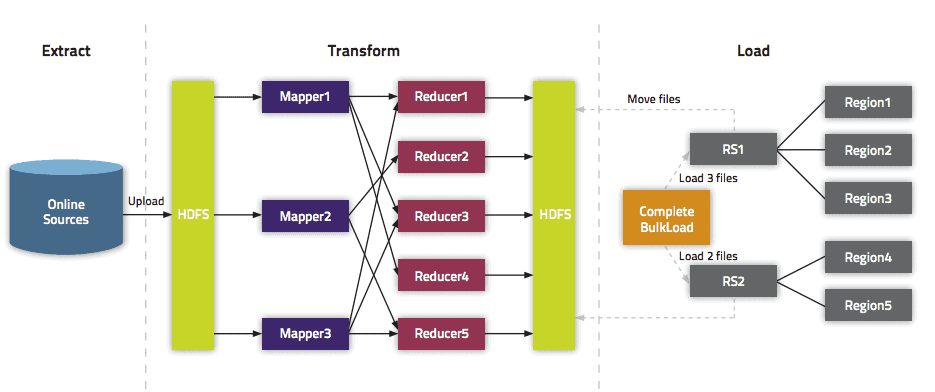
在使用HBase的业务中,很多对HBase写数据的离线任务,因为数据量非常大,可能会造成下面的结果:
- RegionServer频繁flush,从而频繁compact、split,进而影响集群性能。
- RegionServer频繁gc。
- 抢占大量Cpu、内存、IO、带宽资源。
- 甚至会耗尽RegionServer的线程,导致集群阻塞。
以上问题,会影响到离线任务之外的线上任务,很多情况下,这是不能容忍的。所以HBase提供了BulkLoad模式解决这个问题。
BulkLoad方法是通过MapReduce来直接写HFile,跳过了HBase的处理流程。就像在读HBase时候使用Snapshot一样。
BulkLoad核心流程
BulkLoad主要分为两大阶段:HFile生成阶段、HFile导入阶段。
一般去网上搜或者书上介绍的关于BulkLoad相关的文章,在介绍File生成的时候,都会介绍一种非常简单通用的方式,也就是通过MapReduce的方式生成HFile,但是其实HBase核心的BulkLoad过程是不包括HFile生成的,而是HFile导入阶段。
所以说,HFile的生成可以是任何形式的,并不一定是大家所使用的MapReduce形式。
下上面我分别说一下两种不同的方式。
MapReduce生成HFile
因为官方提供了HFileOutputFormat2.configureIncrementalLoad这个工具,所以使用MapReduce方式非常简单,核心代码如下:
public class BulkLoadJob {
static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BulkLoadJob.class);
public static class BulkLoadMap
extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, ImmutableBytesWritable, Put> {
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] valueStrSplit = value.toString().split(",");
String hkey = valueStrSplit[0];
String family = valueStrSplit[1].split(":")[0];
String column = valueStrSplit[1].split(":")[1];
String hvalue = valueStrSplit[2];
/**
* 只支持单列族并发写入,如果是多个列族得多write一次
*/
final byte[] rowKey = Bytes.toBytes(hkey);
final ImmutableBytesWritable HKey = new ImmutableBytesWritable(
rowKey);
Put put = new Put(rowKey);
byte[] cell = Bytes.toBytes(hvalue);
put.add(Bytes.toBytes(family), Bytes.toBytes(column), cell);
context.write(HKey, put);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/**
* 此方法运行不宜小文件使用,每执行一次就会hfile就会增加,可以采用major_compact 'tablename' 进行合并
*/
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
String inputPath = "/tmp/data.txt";
String outputPath = "/tmp/hfiledemo";
String tableName = "hfiletable";
/**
* 删除输出目录
*/
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(conf);
Path outPath = new Path(outputPath);
if (fileSystem.exists(outPath)) {
fileSystem.delete(outPath, true);
}
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "HFile bulk load");
job.setJarByClass(BulkLoadJob.class);
job.setMapperClass(BulkLoadJob.BulkLoadMap.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(ImmutableBytesWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Put.class);
// Disable speculative execution
job.setSpeculativeExecution(false);
job.setReduceSpeculativeExecution(false);
// in/out format
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(HFileOutputFormat2.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outPath);
HTable hTable = new HTable(conf, tableName);
HFileOutputFormat2.configureIncrementalLoad(job, hTable, hTable);
if (job.waitForCompletion(true)) {
/**
* 解决权限问题
*/
FsShell shell = new FsShell(conf);
try {
shell.run(new String[] { "-chmod", "-R", "777", outputPath });
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Couldnt change the file permissions ", e);
throw new IOException(e);
}
/**
* 加载到hbase表
*/
LoadIncrementalHFiles loader = new LoadIncrementalHFiles(conf);
loader.doBulkLoad(outPath, hTable);
}
}
}
其主要步骤就是:
- 配置输入的数据
- 初始化Mapper的Job
- 提交Job
- 等待Job运行结束之后,通过
LoadIncrementalHFiles.doBulkLoad进行加载。
手工生成HFile
上面MapReduce的过程非常简单。但是如果想同时生成多个表,貌似是做不到的。因为这个Reducer只能将数据写入到一个目录里面,而Load的时候,一个目录只能对应一个表。
所以,这种情况,手工生成HFile更方便。可以参考博客:Hbase快速写入解惑之HFile
在阅读HFileOutputFormat2这个工具类的代码之后,发现,其实可以只是用里面createRecordWriter这个方法,稍作修改就可以。
